Vision Services
Diabetic Eye Disease
Patients with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing eye conditions as a complication of their disease. These conditions can lead to vision loss and blindness and include diabetic retinopathy, cataracts and glaucoma. Diabetic retinopathy is actually the leading cause of blindness in the United States.
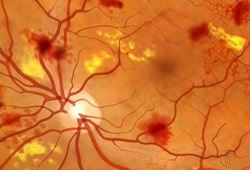
Diabetic eye conditions often develop without any noticeable loss of vision or pain, so significant damage may have occurred by the time patients notice any symptoms. For this reason, it is important for diabetic patients to have their eyes examined at least once a year. Early detection of eye disease can help prevent permanent damage.
Diagnosis of Diabetic Eye Conditions
Diabetic eye conditions can be detected through a comprehensive eye exam. A comprehensive eye exam involves a visual acuity test to measure vision at various distances, and a dilated eye exam to examine the structures of the eye for any signs of disease. During this test, your doctor can examine the retina and optic nerve with a special magnifying lens. Tonometry may also be performed during a comprehensive eye exam to measure the pressure inside the eye with a special instrument.
Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
Other than controlling blood pressure, blood cholesterol and the levels of blood sugar, treatment is not needed during the first three stages of diabetic retinopathy. The fourth stage, proliferative retinopathy is treated with a laser surgery procedure known as scatter laser treatment. During the procedure the abnormal blood vessels are ablated causing them to shrink. This procedure works best once the blood vessels begin to bleed. Severe blood vessel bleeding may need to surgically corrected with a vitrectomy procedure to remove the blood from the eye.
Reducing the Risks of Developing Diabetic Retinopathy
Patients with diabetes need to have an annual comprehensive dilated eye exam. The length of time a patient has diabetes will determine the likelihood of developing diabetic retinopathy. Almost 50 percent of patients in the United States, diagnosed with diabetes, have a form of diabetic retinopathy.
Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical coherence tomography, also known as OCT, is an imaging system that uses light waves to produce a high-resolution view of the cross-section of the retina and other structures in the interior of the eye.
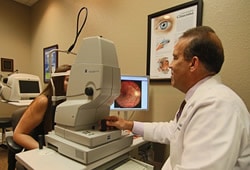
Conditions Detected With an OCT
The images can help with the detection and treatment of serious eye conditions such as:
- Macular hole
- Macular swelling
- Optic nerve damage
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Macular pucker
- Glaucoma
- Cataracts
- Diabetic eye disease
- Vitreous hemorrhage
OCT uses technology that is similar to that of a CT scan of internal organs. With the scattering of light it can rapidly scan the eye to create an accurate cross-section. Each layer of the retina can be evaluated and measured and compared to normal, healthy images of the retina.
The OCT exam takes about 10 to 20 minutes to perform in your doctor's office, and usually requires dilation of the pupils for the best results.
Fundus Photography
A fundus photograph is a specialized form of medical imaging. Using a customized camera with high-powered lenses that are mounted to a microscope, photographs are taken of the back of the eye by focusing light through the cornea, pupil and lens. Fundus photographs are used to identify or monitor a wide variety of ophthalmic conditions.
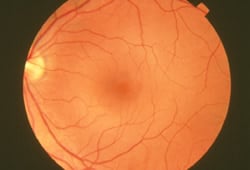
To begin the process, the pupil is dilated with eye drops. The patient will be asked to stare at a fixed device, keeping the eyes focused and still. There will be a series of flashes of light. The process usually takes no more than 10 minutes.
Some of the ophthalmic conditions fundus photography is used for include:
- Glaucoma
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Macular edema
- Microaneurysm
- Optic nerve
Fundus photography has also been used to interpret the results of a fluorescein angiogram.
Corneal Topography
We offer our patients a new ophthalmic diagnostic device called a corneal topographer. This device measures the curvature and shape of the cornea and displays color coded maps. The cornea is the front window part of the eye which we see thru. The cornea is two thirds of the refractive power of the eye. The corneal topographer helps to identify normal and abnormal corneas and diagnose eye disease along with optimizing contact lens prescribing with efficient lens selection and fitting.
If you would like more information about our Vision Services or to schedule an appointment, feel free to fill out our convenient contact form or call us directly at 727-674-2500.